The War That Changed the World (1914–1918)
“The lamps are going out all over Europe; we shall not see them lit again in our lifetime.”
— Sir Edward Grey, British Foreign Secretary, 1914
Introduction
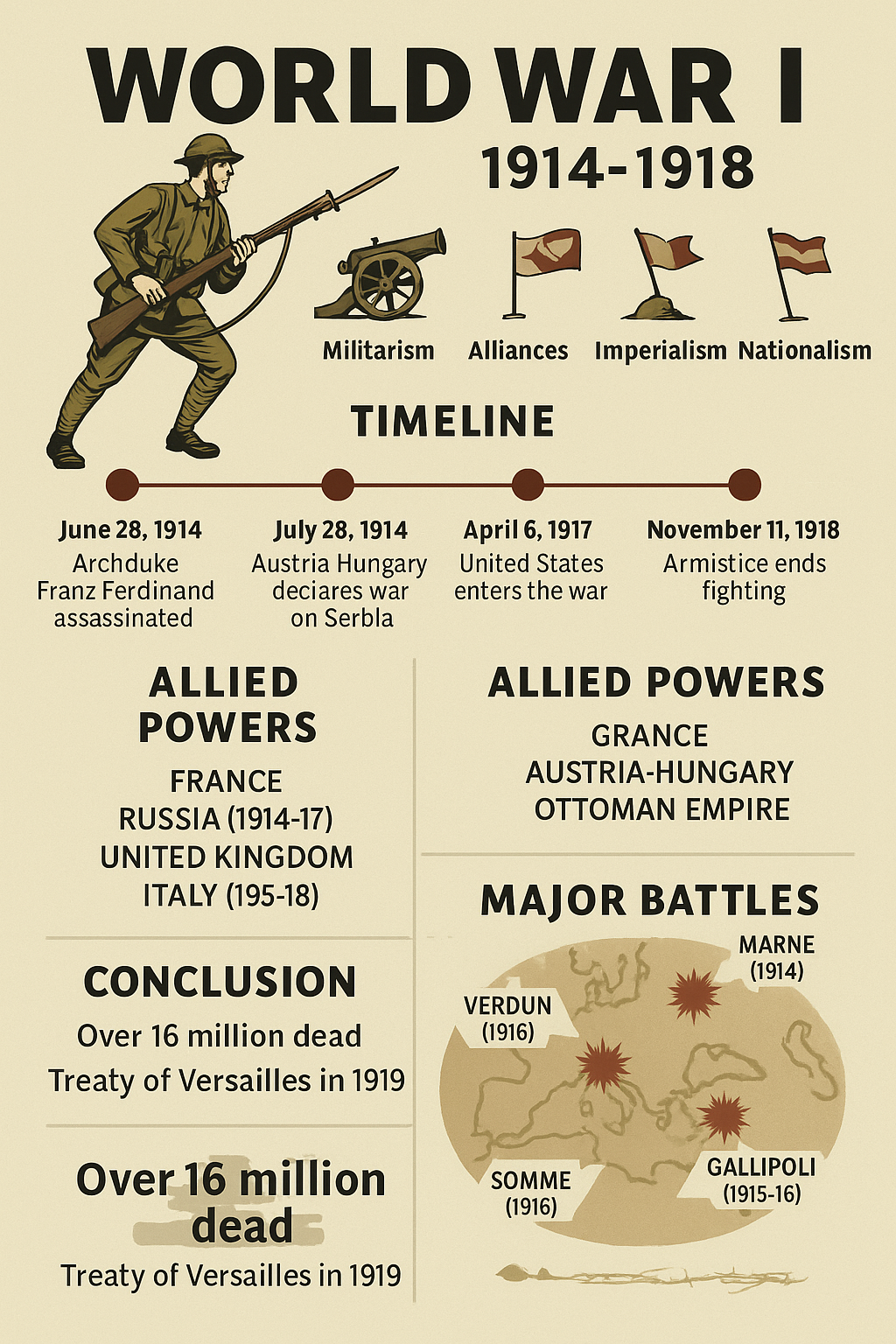
World War I, also known as the Great War, was one of the deadliest wars in human history. It lasted from 1914 to 1918 and involved more than 30 countries. Over 16 million people lost their lives. This war reshaped national boundaries, political systems, and the global balance of power. In this article, we explain World War I in a simple, easy-to-understand manner.
Causes of World War I
The war did not start overnight. It was the result of rising tensions, political mistakes, and power struggles that had been building for years. The main causes were:
Militarism
European nations were building large armies and competing to have the best weapons. This race made war more likely.
Alliances
Countries formed secret or open military alliances. For example:
- Allied Powers: France, Britain, Russia (later joined by the United States and others)
- Central Powers: Germany, Austria-Hungary, Ottoman Empire
If one country was attacked, its allies would jump in, turning a small conflict into a global war.
Imperialism
European powers competed for colonies in Africa, Asia, and other parts of the world. This created tension and mistrust between nations.
Nationalism
People were extremely proud of their countries and believed they were superior. In places like the Balkans, smaller groups wanted independence, especially from Austria-Hungary.
The Spark: Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
On June 28, 1914, Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary was assassinated in Sarajevo by Gavrilo Princip, a Bosnian Serb nationalist. This event triggered a chain of alliances:
- Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia.
- Russia came to Serbia’s defense.
- Germany backed Austria-Hungary.
- France and Britain joined against Germany.
In just a few weeks, much of the world was at war.
The Nature of the War
Trench Warfare
World War I was known for trench warfare. Soldiers dug long trenches in the ground and lived in terrible conditions—mud, rats, disease, and constant fear of shelling. The area between opposing trenches was called “No Man’s Land” and was extremely dangerous.
New Weapons
World War I saw the use of modern technologies:
- Machine guns
- Poison gas (chlorine, mustard gas)
- Submarines (U-boats)
- Tanks
- Aircraft
These made the war more deadly than any before.
Major Battles
- Battle of the Marne (1914): Stopped the German advance into France.
- Battle of Verdun (1916): One of the longest and bloodiest battles.
- Battle of the Somme (1916): Over one million casualties.
- Gallipoli Campaign (1915): Failed Allied attempt to control the sea route to Russia.
India’s Role in World War I
India, under British rule, played a major role in World War I. Over 1.3 million Indian soldiers and laborers were sent to fight in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. Indian soldiers fought bravely in:
- France and Belgium (Western Front)
- Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq)
- East Africa and Gallipoli
More than 74,000 Indian soldiers lost their lives. India also supplied food, money, and materials to support the British war effort.
The United States Enters the War
At first, the United States remained neutral. But several factors pulled it into the war in 1917:
- German submarines sank American ships, killing civilians.
- The Zimmermann Telegram: Germany secretly tried to convince Mexico to attack the USA.
- Economic and political pressure.
American troops gave the Allies fresh strength and helped push back the German forces.
The End of the War
By 1918, the Central Powers were exhausted. Germany faced internal protests, food shortages, and loss of allies. On November 11, 1918, Germany signed an armistice. The fighting stopped at 11 AM on the 11th day of the 11th month. This day is now known as Armistice Day or Veterans Day in many countries.
The Treaty of Versailles (1919)
After the war, the victorious countries met in Paris to decide the future. The Treaty of Versailles was signed in 1919. The main points were:
- Germany had to accept full blame for the war.
- Germany had to pay huge reparations (money for damages).
- Germany lost territory and its overseas colonies.
- Its military was heavily restricted.
The treaty angered many Germans and is often considered a major reason for the rise of Adolf Hitler and World War II.
Effects of the War
Human Loss
More than 16 million people died, and 20 million were wounded. Entire towns and cities were destroyed.
Political Changes
Four major empires collapsed:
- German Empire
- Austro-Hungarian Empire
- Ottoman Empire
- Russian Empire
This led to the creation of many new countries in Europe and the Middle East.
Economic Damage
The war caused massive economic problems. Inflation, unemployment, and poverty increased in many nations, especially in Germany.
Social Changes
Women entered the workforce in large numbers. Their contribution led to greater demands for women’s rights, including the right to vote.
The League of Nations
An early version of the United Nations, it was created to maintain peace and prevent future wars. However, it lacked power and failed to stop World War II.
Lessons from World War I
World War I taught the world many important lessons:
- War causes massive suffering and destruction.
- Peace treaties must be fair and balanced.
- International cooperation is essential to prevent future wars.
- Nationalism and hatred can lead to disaster.
Conclusion
World War I was not just a war between countries. It was a global crisis that affected millions of lives, changed political borders, and altered world history. Its causes, events, and consequences continue to influence modern politics, diplomacy, and society. It reminds us that peace must never be taken for granted.
Let us remember the sacrifices of those who fought and died, and work together to build a more peaceful and just world.